Challenges and Potential Solutions to Landfill Methane Emissions
Key Takeaways
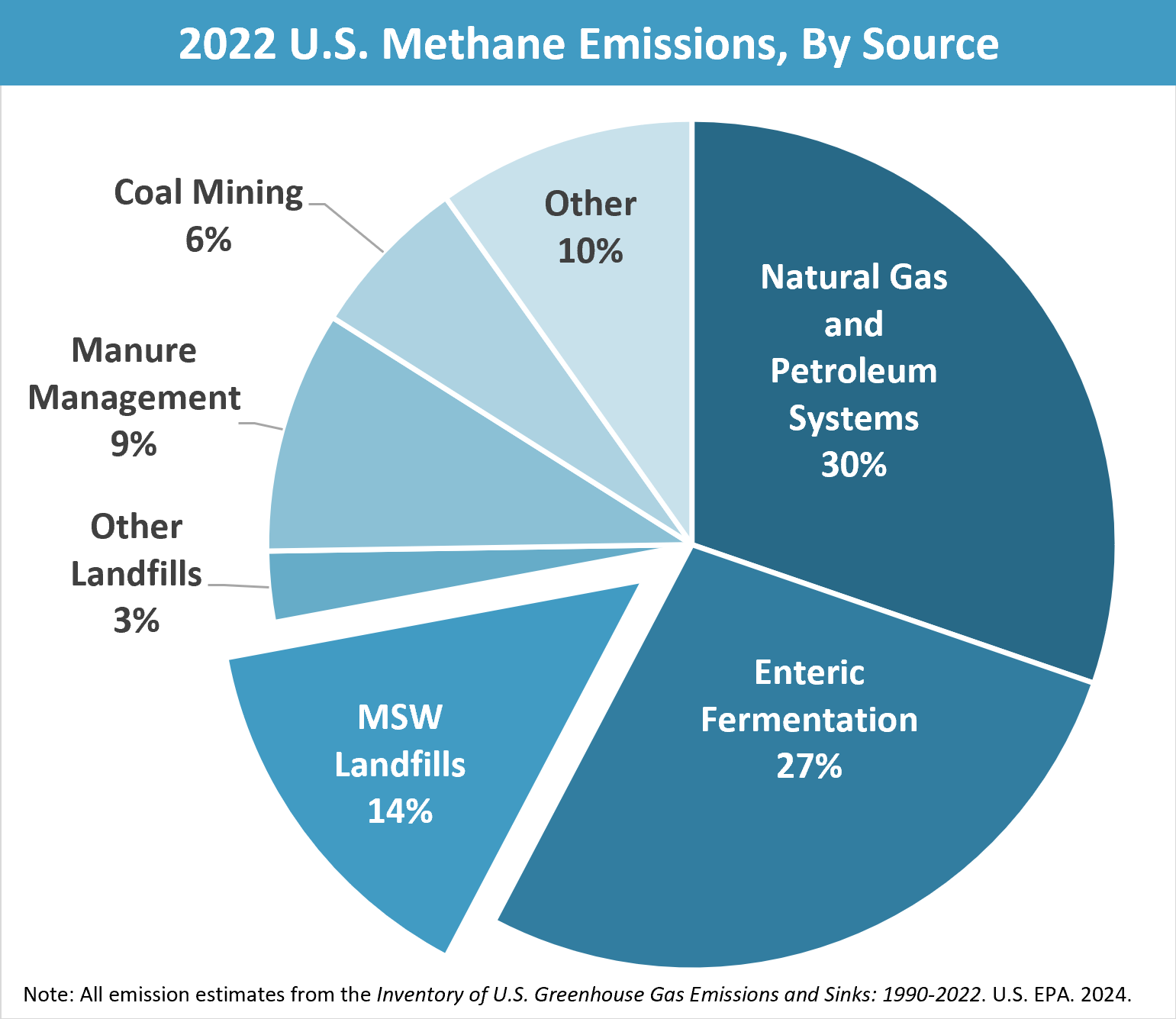
- Methane emissions from landfills account for approximately 14.4% of human-related methane emissions in the U.S.
- Methane is over 25 times more potent than carbon dioxide in trapping heat in the atmosphere.
- Effective methane management includes capturing and utilizing landfill gas as a renewable energy source.
- Reducing organic waste and improving recycling can significantly lower methane emissions from landfills.
- Community involvement and policy regulations are crucial in mitigating landfill methane emissions.
Methane: A Hidden Threat from Landfills
When we think of landfills, we often imagine piles of waste and the smell of decay. However, there's an invisible threat lurking in these vast waste repositories: methane gas. Methane is a powerful greenhouse gas, significantly contributing to global warming. While it's colorless and odorless, its effects are anything but invisible.
Methane's Environmental Impact
Methane is a greenhouse gas that is over 25 times more effective than carbon dioxide at trapping heat in the atmosphere over a 100-year period. This makes it a major player in climate change. When organic waste, like food scraps and yard trimmings, decomposes anaerobically (without oxygen) in landfills, methane is produced. This gas then escapes into the atmosphere, contributing to the greenhouse effect.
“Basic Information about Landfill Gas …” from www.epa.gov and used with no modifications.
Health Risks Associated With Methane Emissions
Besides its environmental impact, methane emissions pose direct health risks. Methane itself is not toxic, but it can displace oxygen in the air, leading to suffocation in confined spaces. Moreover, the process of methane production in landfills can release other harmful gases, such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which can cause respiratory problems and other health issues for nearby communities.
Current Global Emission Statistics
Globally, landfills are the third-largest source of methane emissions. In the United States alone, municipal solid waste (MSW) landfills accounted for approximately 14.4% of human-related methane emissions in 2022. This significant contribution underscores the importance of addressing methane emissions from landfills to combat climate change effectively.
“Municipal solid waste landfills are the third-largest source of human-related methane emissions in the United States, accounting for approximately 14.4 percent of these emissions in 2022.”

“Landfill Gas Monitoring Systems …” from www.geoengineer.org and used with no modifications.
Sources and Causes of Landfill Methane Emissions
Understanding the sources and causes of methane emissions from landfills is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies. Methane production in landfills primarily results from the anaerobic decomposition of organic waste. However, several factors influence the rate and volume of methane emissions.
Decomposition of Organic Waste
Organic waste, such as food scraps, paper, and yard trimmings, makes up a significant portion of landfill content. When these materials break down in the absence of oxygen, they produce methane. This process is natural but can be accelerated by certain conditions, such as high moisture levels and warm temperatures.
Factors That Increase Methane Production
Several factors can increase the production of methane in landfills. These include the composition of the waste, the landfill's moisture content, and temperature. High moisture levels can enhance microbial activity, leading to faster decomposition and more methane production. Similarly, warmer temperatures can increase the rate of organic matter breakdown.

“Landfill Methane Emissions by World …” from www.researchgate.net and used with no modifications.
Role of Landfill Design and Management Practices
Landfill design and management practices play a significant role in methane emissions. Properly designed landfills can minimize methane production by controlling the decomposition process. This includes managing moisture levels, waste compaction, and implementing gas collection systems. Conversely, poorly managed landfills can become significant sources of methane emissions.
“Where sanitary landfills exist — commonly in developed economies — policies should require best practices for methane management during design and operations, including comprehensive emissions monitoring.”
Adopting Advanced Landfill Designs
Advanced landfill designs are pivotal in reducing methane emissions. These designs focus on optimizing waste decomposition and gas collection. One such approach is the use of bioreactor landfills, which enhance the decomposition process by adding moisture and nutrients. This not only accelerates the breakdown of organic matter but also increases the efficiency of methane capture.
Another innovative design is the use of vertical wells and horizontal collectors to efficiently capture methane gas. By strategically placing these systems within the landfill, operators can maximize gas collection, reducing the amount of methane that escapes into the atmosphere. This proactive approach not only mitigates environmental impact but also transforms potential waste into a valuable energy resource.
Encouraging Consumer Participation in Waste Reduction
Consumers play a crucial role in reducing landfill methane emissions. By making conscious choices about waste, individuals can significantly impact the volume of organic material sent to landfills. Simple actions, like composting food scraps and yard waste, can drastically reduce the amount of methane-producing material in landfills.
Moreover, consumers can participate in recycling programs, reducing the need for raw materials and lowering overall waste production. By understanding and practicing waste separation, individuals ensure that recyclables are not contaminated, making recycling processes more efficient.
Community education and awareness programs are vital in fostering these habits. Workshops, informational campaigns, and school programs can educate the public on the importance of waste reduction and its direct impact on methane emissions. As more people adopt these practices, the collective effect can lead to a significant decrease in landfill methane emissions.
Real-Life Success Stories and Case Studies
Examining real-life examples of successful methane reduction initiatives provides valuable insights into effective strategies and their outcomes. These stories demonstrate the power of innovation and collaboration in addressing environmental challenges.
Sunshine Canyon Landfill Transformation
Sunshine Canyon Landfill in California is a prime example of effective methane management. By implementing a comprehensive gas collection system, the landfill has significantly reduced its methane emissions. The captured gas is then converted into electricity, providing power to thousands of homes in the area. For more information on landfill gas management, visit the EPA's website.
This transformation was made possible through the collaboration of local government, landfill operators, and energy companies. Their joint efforts have not only reduced greenhouse gas emissions but also turned a potential environmental hazard into a renewable energy source, showcasing the potential of landfill gas-to-energy projects.

“Sunshine Canyon Landfill Methane Leak …” from downtownlalaw.com and used with no modifications.
Innovative Practices in European Landfills
In Europe, several landfills have adopted innovative practices to minimise methane emissions. For instance, the Albury Landfill in the UK uses a state-of-the-art gas management system that captures over 90% of the methane produced. This system includes advanced gas wells and monitoring technology to ensure efficient gas collection and utilisation.
Additionally, many European countries have implemented strict regulations on organic waste disposal, encouraging composting and waste separation at the source. These policies have led to a significant reduction in landfill methane emissions, demonstrating the effectiveness of regulatory measures combined with technological advancements.

“Albury landfill site …” from www.getsurrey.co.uk and used with no modifications.
Community-Driven Initiatives
Community-driven initiatives have also proven successful in reducing methane emissions. In some regions, local communities have taken the lead in organizing waste reduction programs and promoting sustainable practices. For example, the Zero Waste initiative in San Francisco aims to divert all waste from landfills by promoting recycling, composting, and responsible consumption.
These grassroots efforts highlight the power of community involvement in environmental conservation. By working together, residents can create meaningful change, reducing landfill methane emissions and contributing to a healthier planet.

“Toward Zero Waste | SPUR” from www.spur.org and used with no modifications.
The Role of Policy and Regulation
Policies and regulations play a critical role in managing methane emissions from landfills. By setting standards and guidelines, governments can drive change and encourage the adoption of best practices in waste management.
Effective regulations require landfill operators to implement methane capture and utilization systems, ensuring that emissions are minimized. These policies also promote transparency and accountability, requiring regular monitoring and reporting of methane emissions.
Importance of Stronger Regulations
Stronger regulations are essential in addressing the global methane emissions challenge. By enforcing stricter limits on emissions and requiring advanced gas collection systems, governments can ensure that landfills operate sustainably. These regulations also encourage investment in research and development of new technologies, driving innovation in methane management.
Global Agreements and Promises
International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, highlight the global commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. These agreements set targets for methane reduction and encourage countries to adopt policies and practices that align with these goals. By working together, nations can address the methane emissions challenge on a global scale, sharing knowledge and resources to achieve common objectives. For instance, understanding the outcomes of COP26 pledges can provide insights into how countries are progressing towards these targets.
Such agreements also foster collaboration between countries, promoting the exchange of best practices and technological advancements. This international cooperation is vital in tackling methane emissions and mitigating climate change. For instance, initiatives like COP26 pledges have been instrumental in driving global efforts to reduce emissions.

“Turning COP26 methane promises into …” from blogs.edf.org and used with no modifications.
The Role of Governments and NGOs
Governments and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) play a crucial role in methane emissions management. By providing funding and resources, they support research and development of innovative technologies and practices. Additionally, they facilitate collaboration between stakeholders, including landfill operators, energy companies, and local communities.
NGOs also raise awareness about the importance of reducing methane emissions, advocating for policy changes and promoting sustainable practices. Their efforts help to educate the public and encourage individuals to take action in reducing their environmental impact.
Future Perspectives and Innovations
Looking ahead, the future of methane emissions management holds promise. With continued advancements in technology and increased awareness, significant progress can be made in reducing landfill methane emissions.
Technological Advancements in Methane Management
Technological advancements are at the forefront of methane management. New technologies, such as enhanced gas collection systems and advanced monitoring tools, are improving the efficiency of methane capture and utilization. These innovations enable landfill operators to minimize emissions and maximize energy recovery.
Moreover, research into alternative waste management methods, such as anaerobic digestion and waste-to-energy technologies, offers new opportunities for reducing methane emissions. By exploring these options, we can develop sustainable solutions that address the environmental challenges posed by landfills.
In conclusion, addressing methane emissions from landfills requires a multifaceted approach. By adopting advanced landfill designs, encouraging consumer participation, and implementing effective policies and regulations, we can significantly reduce methane emissions and mitigate their impact on the environment. Through collaboration and innovation, we can create a sustainable future for generations to come.
Potential of Renewable Energy from Landfill Methane
Landfill methane offers a unique opportunity to produce renewable energy. When captured effectively, this methane can be used to generate electricity, heat, or even as a vehicle fuel. This process not only mitigates harmful emissions but also provides a valuable energy resource. Learn more about landfill gas to energy and its benefits.
Many landfills are already capitalizing on this potential. By installing gas collection systems and utilizing technologies like microturbines and gas engines, they convert methane into electricity. This renewable energy can then be supplied to local grids, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and contributing to a cleaner energy future.

“Landfill Gas | Green Power EMC” from greenpoweremc.com and used with no modifications.
Research and Development in Methane Capture
Ongoing research and development are crucial in enhancing methane capture technologies. Scientists and engineers are exploring new methods to increase the efficiency of gas collection systems and reduce costs. Innovations such as biofilters and advanced membrane technologies hold promise for improving methane capture rates.
Collaboration between research institutions, industry, and government is essential to drive these advancements. By investing in research and supporting pilot projects, we can accelerate the development of cutting-edge solutions that address the challenges of methane emissions from landfills.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
Addressing methane emissions from landfills is a critical component of our efforts to combat climate change. By taking action now, we can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and protect our planet for future generations. It's time to harness the potential of landfill methane and turn this environmental challenge into an opportunity for sustainable growth.
The Importance of Collective Efforts
Success in reducing methane emissions requires collective efforts from all stakeholders. Governments, industry, communities, and individuals must work together to implement effective strategies and technologies. By pooling resources and knowledge, we can make significant strides in mitigating the impact of landfill methane.
The Power of Individuals and Communities
Individuals and communities have a vital role to play in reducing methane emissions. Simple actions, such as composting organic waste and supporting recycling programs, can make a significant difference. By raising awareness and advocating for sustainable practices, communities can drive change and contribute to a healthier environment.
Moreover, community-led initiatives can inspire others and demonstrate the power of grassroots action. When people come together with a common purpose, they can achieve remarkable results and create lasting change.
Frequently Asked Questions
As we strive to address methane emissions from landfills, it's essential to understand the underlying issues and solutions. Here are some common questions and answers to help clarify the topic.
What is the primary source of methane in landfills?
The primary source of methane in landfills is the anaerobic decomposition of organic waste. When organic materials like food scraps and yard waste break down without oxygen, they produce methane gas.
How does methane contribute to climate change?
- Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, trapping heat in the atmosphere more effectively than carbon dioxide.
- Its high global warming potential makes it a significant contributor to climate change.
- Reducing methane emissions can have a rapid and substantial impact on slowing global warming.
By addressing methane emissions, we can mitigate its effects and work towards a more sustainable future. Learn more about methane from landfills and its impact.
What are some successful methods of capturing landfill methane?
Successful methods of capturing landfill methane include installing gas collection systems, such as wells and pipes, to extract the gas from the landfill. These systems can be connected to energy conversion technologies like turbines or engines to generate electricity.
Additionally, some landfills use biofilters or other advanced technologies to improve methane capture efficiency and reduce emissions further.
Why do some landfills pose more risks than others?
Several factors can make some landfills more risky in terms of methane emissions:
- Poorly managed landfills may lack proper gas collection systems, allowing more methane to escape.
- The composition and moisture content of the waste can affect methane production rates.
- Geographic and climatic conditions, such as temperature and humidity, can influence methane emissions.
By implementing best practices and advanced technologies, these risks can be mitigated, reducing the environmental impact of landfills.
What can individuals do to help reduce landfill methane emissions?
Individuals can take several actions to help reduce landfill methane emissions, such as supporting initiatives for landfill methane capture and advocating for better waste management practices.
First, practice waste reduction by composting organic materials at home. This keeps organic waste out of landfills, reducing methane production.
Second, participate in local recycling programs to divert waste from landfills and reduce the need for new raw materials.
Lastly, support policies and initiatives that promote sustainable waste management practices, such as advocating for composting facilities and improved landfill designs in your community.
US Landfill Gas Resources: A Booming Green Energy Sector
Untapped U.S. Landfill Gas Resources are an Opportunity for Green Investment The American landfill gas (LFG) sector has seen a big change in recent years. It's now a key player in the country's biogas world. Even though it's only 23% of over 2,500 biogas systems now installed nationwide, it captures 72% of all biogas by […]
Landfill Gas Management Solutions
You know the tough part about landfill gas is that the problems rarely show up one at a time. Odors, off-site migration concerns, wellfield instability, and methane emissions can all trace back to the same root issue: gas is finding an easier path than the one you built for it. All this leads to the […]
Gas Flare Systems: Enhancing Safety and Efficiency in Landfill Gas Operations
Proper landfill gas flare systems can achieve up to 99.5% methane destruction efficiency, reducing environmental impacts. Enclosed systems enhance emission control. Safety features like flame arrestors prevent incidents. Flares integrate with energy recovery, transforming waste gases into renewable resources, offering compliance and sustainability benefits for landfill operations…
Best Enclosed Landfill Gas Flare Stack Suppliers & Manufacturers
Enclosed landfill gas flares are crucial for sustainable waste management, offering up to 99.9% methane destruction. Top suppliers like John Zink and Zeeco provide advanced systems with features minimizing emissions. Compliance is easier with these solutions, ensuring effective gas management and environmental protection…








